How robotics can reduce firefighter injuries?
07/03/2025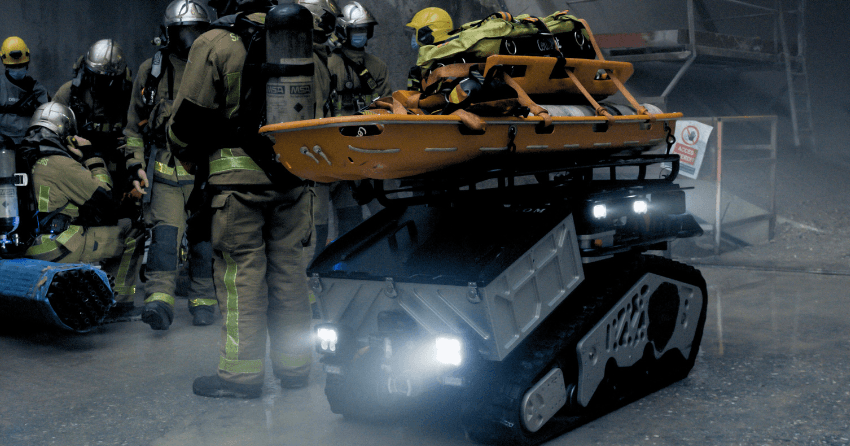
Firefighting is one of the most dangerous professions in the world, with high rates of injuries and fatalities every year. As fire departments search for safer, more effective solutions, robotic technology is emerging as a game-changer in emergency response. From fire suppression robots to remote-controlled surveillance drones, these advanced tools are helping to reduce firefighter injuries, limit human exposure to danger, and increase operational efficiency. In this article, we explore how robotics is transforming firefighting and protecting those who protect us.
Firefighter safety, a major challenge
Statistics on firefighter injuries and fatalities
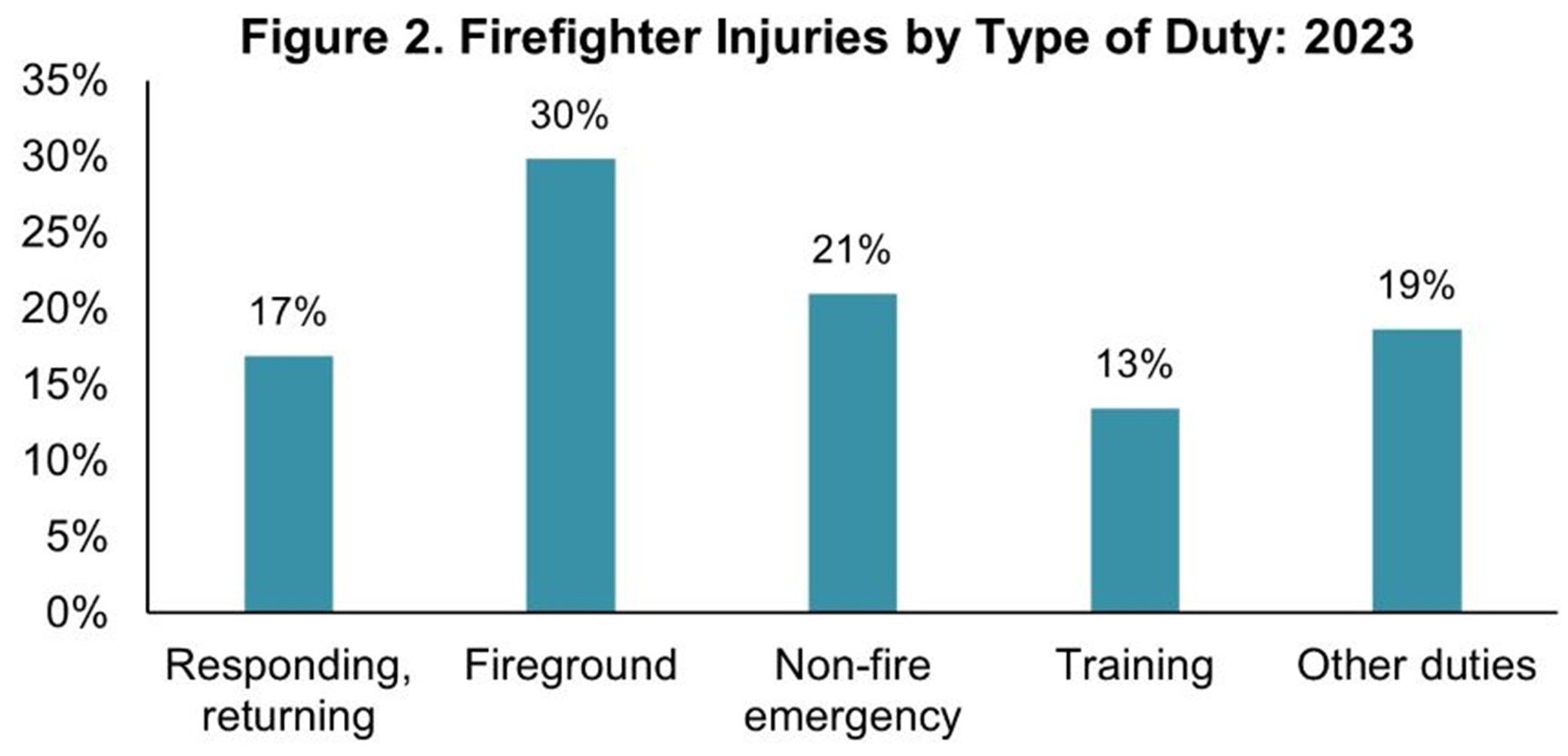
Firefighting is one of the most dangerous yet essential professions in the world. As the frequency and intensity of fires increase, driven by climate change and technological hazards,firefighter safety becomes more critical than ever. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), more than 63,000 firefighters were injured in the United States in 2023. Nearly 30% of these injuries occurred during fireground operations, making this phase the most dangerous part of their job.
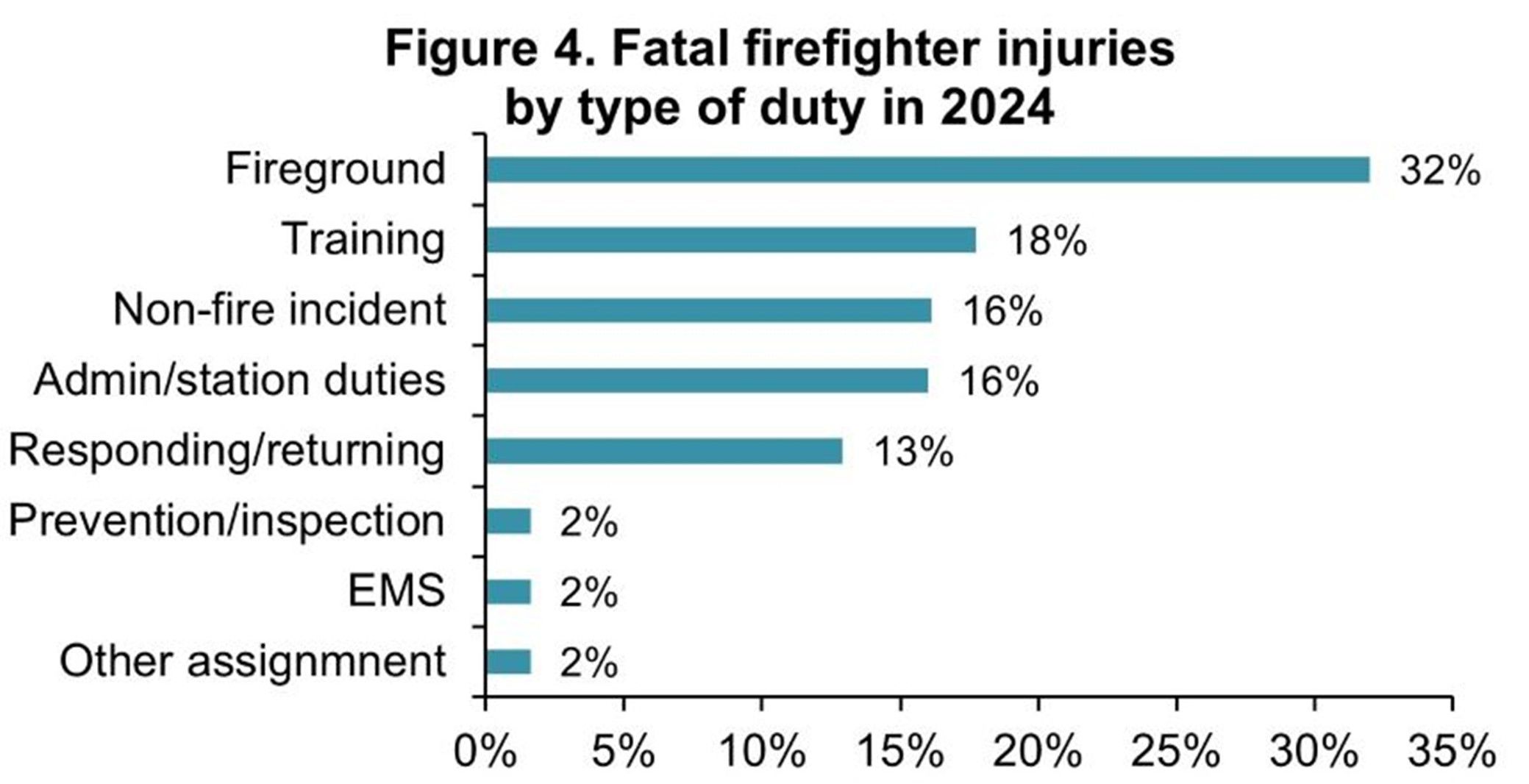
When it comes to fatalities, the statistics are pointing the same way. In 2024, 62 US firefighters lost their lives in the line of duty, with 32% of fatal incidents occurring during fireground operations. This is by far the highest proportion among all types of firefighter duties.
The dangers faced on the field
These numbers highlight an urgent need for innovative safety measures and advanced technologies to reduce exposure and better protect those on the front lines. The dangers faced on the field Fires are unpredictable and brutal environments. As illustrated in recent reports, over 18,000 injuries occurred specifically during fire interventions. The top causes of injury include: • Fire burn • Chemical burns • Inhalation of smoke or toxic gases • Thermal stress
While burns and fire-related injuries often have immediate effects,** smoke and gas inhalation pose long-term health risks**, potentially leading to chronic respiratory issues or even cancer. According to NIOSH, firefighters face a 9-14% greater risk of lung cancer, while certain studies suggest risks as high as 30-50% for other cancers like mesothelioma and bladder cancer, though these percentages can differ by country and population studied.
Each fire presents its own set of challenges. Confined fires, such as those in parking garages, tunnels, or high-rise buildings, are particularly hazardous. They can cause: • Rapid temperature escalation • Limited visibility • Oxygen depletion • Toxic smoke buildup • Increased risk of structural collapse
The role of robotics for reducing firefighter injuries
Remote fire suppression
In high-risk environments such as industrial fires, tunnel fires, or wildfires, remote fire suppression is proving to be a game-changer. Advance Robotic devices like firefighting robots and drones now offer a safer, more efficient alternative by tackling flames without putting human crews at risk. These machines can be deployed in the early stages of an incident, creating a protective buffer between the fire and the responders.
Ground-based robots like Colossus and Rhyno Protect, being developed by Shark Robotics, are designed to approach the fire source and suppress it using high-powered water or foam cannons, all while being remotely operated from a secure distance (up to 1km). This drastically reduces the risk of burn injuries, smoke inhalation, and thermal stress during initial attack phases.
These robots are not just powerful, they are also highly maneuverable, capable of passing through standard doorways, which makes them ideal for indoor interventions such as warehouse fires, industrial sites, and other confined environments. Their precision targeting ensures more effective flame suppression with less water waste and minimal collateral damage.
Monitoring and data collection in hazardous environments
Before entering a burning or unstable structure, having access to real-time data and visual feedback is essential for effective incident management. Firefighting robots equipped with advanced sensors and HD cameras can be deployed ahead of the crew to assess critical risks such as dense smoke, explosion hazards, or toxic gas presence, conditions that would otherwise endanger people's lives.
The Colossus robot, for example, is fitted with a thermal camera that allows teams to monitor temperature levels in real time, even through smoke. It also features an integrated sensor box with an additional HD camera, designed to be modular and customizable. Firefighters can install their own field-specific sensors, such as gas detectors, radiation monitors, depending on the nature of the incident. This modularity ensures that the robot adapts to a wide variety of hazardous situations.
All collected data is transmitted live to the Shark Station, the portable control interface used by firefighters to operate the robot remotely. From this rugged tablet-based platform, teams can monitor multiple data streams, including video, environmental conditions, and telemetry. This provides full situational awareness without requiring anyone to physically enter the danger zone. This level of remote control and centralized information about the situation enables commanders to make faster, more accurate tactical decisions as the situation evolves, keeping people safe while optimizing efficiency on the ground. In low-visibility environments or structurally unstable settings, robotic support like Colossus is no longer a luxury, it's a critical asset in modern firefighting.
Evacuation and rescue assistance
Beyond fire suppression, robotics is also revolutionizing evacuation operations. Robots like Colossus, Rhyno Protect, and Barakuda are modular and can be adapted with features such as stretchers to assist with the extraction of injured civilians or firefighters from dangerous zones. Without tools, and just in a few seconds, the robot can be reassessed by changing the equipment. These systems allow for rapid victim transport without putting additional responders at risk, particularly valuable when navigating through toxic smoke, falling debris, or high-heat environments. This functionality supports emergency responders during mass casualty events or in areas that are otherwise inaccessible due to fire or structural instability.
Increased operational efficiency
The benefits of firefighting robots go beyond safetythey also contribute to greater operational efficiency. These machines allow for precise and targeted action, minimizing damage while optimizing the use of resources. One standout advantage: robotic operations can use up to 10 times less water than traditional firefighting methods. By targeting the fire source more accurately and operating continuously without fatigue, robots help reduce waste, preserve water reserves, and lower the overall environmental impact of interventions. In short, firefighting robots enhance safety, improve efficiency, and bring intelligent decision-making to the frontline, all while reducing the physical toll on human teams.
Case study : the Colossus firefighting robot at Notre Dame
On April 15, 2019, alarms rang out in the cathedral. By 6:50 p.m., smoke billowed from the roof, marking the beginning of a fire that would consume the ancient wooden framework, nicknamed "the forest" for its medieval timber beams. Within two hours, the flames reached the spire, which collapsed at 7:50 p.m., leaving onlookers stunned. With temperatures exceeding 900°C (1652.0 °F), molten lead was flowing inside the cathedral, the nave's roof was threatening to collapse : any human intervention had become impossible., the task of containing the blaze while protecting the cathedral’s towers and relics presented important challenges for the firefighters. Operating for nearly 10 hours, Colossus delivered cooling power equivalent to 15 firefighters, stabilizing a critical situation while safeguarding human lives. According to the spokesperson for the Paris Fire Brigade, the Colossus robot "helped extinguish the fire and lower the temperature inside the nave" during the Notre-Dame fire.
The challenges and future perspectives of robotics
Current limitations
While the operational autonomy of the robotic devices (up to 12 hours) may be limited, they have already proven invaluable in reducing the physical toll on human firefighters, especially in reducing injuries and improving safety. However, contact with humans is still essential, as these robots cannot operate entirely autonomously in complex or unpredictable scenarios. Although robotic devices are being developed to become more efficient and modular, they are still not as adaptable as humans. They are less mobile and cannot make independent decisions, nor can they switch tasks without human intervention. This means that while they significantly assist with specific tasks like fire suppression and hazardous material detection, their role in firefighting is still complementary to human expertise.
Evolving towards greater autonomy
Despite these limitations, there is significant potential for new technology to further benefit firefighter safety and operational effectiveness. Artificial intelligence (AI) and human-robot collaboration are the next frontiers in the evolution of firefighting robots. In the future, AI will enable robots to perform more autonomous decision-making, enhancing their ability to operate in complex, unpredictable environments. Through machine learning, robots will be able to adapt to various fire scenarios and predict risks, thereby improving safety for both the robot and the crew. Human-robot collaboration is another key development that will assist with improving efficiency on the fireground. By allowing robots to handle the most dangerous tasks, such as fire suppression, search and rescue, or toxic gas monitoring, human firefighters can focus on other critical aspects of the operation, ensuring that all personnel remain safe while working together in harmony.
Upcoming innovations from Shark Robotics
At Shark Robotics, we are committed to staying at the forefront of firefighting technology. Our ongoing developments focus on enhancing the autonomy and adaptability of our robots, ensuring they meet the increasing demands of modern firefighting while supporting firefighters on the ground. One of the key features of our robots is their modularity. For example, the Colossus robot already offers 10 different mission modules, each designed to adapt to a wide range of firefighting scenarios. Whether it's for fire suppression, search and rescue, or handling hazardous materials, these modules allow our robots to be highly customizable, meeting the specific needs of each mission. We are continuously developing new modules to address emerging challenges and meet firefighters' needs in various environments. Looking ahead, we are particularly excited about our work on the first autonomous irefighting robot designed specifically for confined environments. Using artificial intelligence, this innovative robot will be able to spot fires and act quickly to begin suppression efforts, providing critical support to human crews. The goal of this autonomous robot is not to replace human firefighters, but to assist them by acting rapidly in dangerous situations, helping to contain the flames and reduce risks to human life in hard-to-reach areas.
Questions
What is a firefighting robot ?
A firefighting robot is an advanced, remote-controlled or autonomous machine designed to assist in fire response and suppression efforts. These robots are equipped with specialized sensors, cameras, and firefighting equipment, such as high-powered water or foam cannons. They are deployed in hazardous environments, such as burning buildings, industrial sites, or forest fires, where human firefighters would be at high risk. Firefighting robots can perform tasks like fire suppression, hazardous material detection, search and rescue operations, and even monitoring dangerous conditions such as smoke, gas levels, and structural integrity. The key benefit of these robots is their ability to enter dangerous areas, provide real-time data, and perform firefighting tasks without putting human lives at risk.
Can robots replace firefighters ?
While firefighting robots provide invaluable support in dangerous situations, they are not designed to fully replace human firefighters. The role of robots is to assist by acting quickly in high-risk environments, such as containing fires or gathering critical data, which helps firefighters make informed decisions while keeping them safe. Firefighters will always be essential for tasks that require human judgment, leadership, and on-the-ground decision-making. For a deeper dive into the relationship between robots and human firefighters, and to understand how robots will work alongside humans rather than replace them, check out our article on The Future of Fire Interventions: Robots or Humans?.
Contact our communications team
